What Is Screw Pitch? The Different of Lead and Pitch
Screw Lead, Screw pitch, and Thread starts
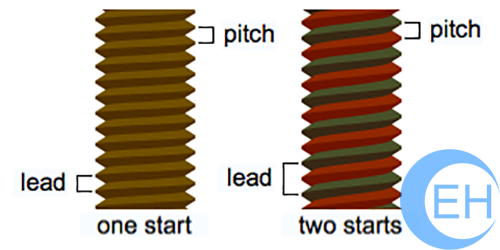
Lead and pitch for two screw threads; one with one start and one with two starts.
Lead and pitch are closely related concepts. They can be confused because they are the same for most screws. Lead is the distance along the screw’s axis that is covered by one complete rotation of the screw (360°). Pitch is the distance from the crest of one thread to the next. Because the vast majority of screw threadforms are single-start threadforms, their lead and pitch are the same. Single-start means that there is only one “ridge” wrapped around the cylinder of the screw’s body. Each time that the screw’s body rotates one turn (360°), it has advanced axially by the width of one ridge. “Double-start” means that there are two “ridges” wrapped around the cylinder of the screw’s body. Each time that the screw’s body rotates one turn (360°), it has advanced axially by the width of two ridges. Another way to express this is that lead and pitch are parametrically related, and the parameter that relates them, the number of starts, very often has a value of 1, in which case their relationship becomes equality. In general, lead is equal to pitch times the number of starts.
Whereas metric threads are usually defined by their pitch, that is, how much distance per thread, inch-based standards usually use the reverse logic, that is, how many threads occur per a given distance. Thus inch-based threads are defined in terms of threads per inch (TPI). Pitch and TPI describe the same underlying physical property—merely in different terms. When the inch is used as the unit of measurement for pitch, TPI is the reciprocal of pitch and vice versa. For example, a 1⁄4-20 thread has 20 TPI, which means that its pitch is 1⁄20 inch (0.050 in or 1.27 mm).
As the distance from the crest of one thread to the next, pitch can be compared to the wavelength of a wave. Another wave analogy is that pitch and TPI are inverses of each other in a similar way that period and frequency are inverses of each other.